Description
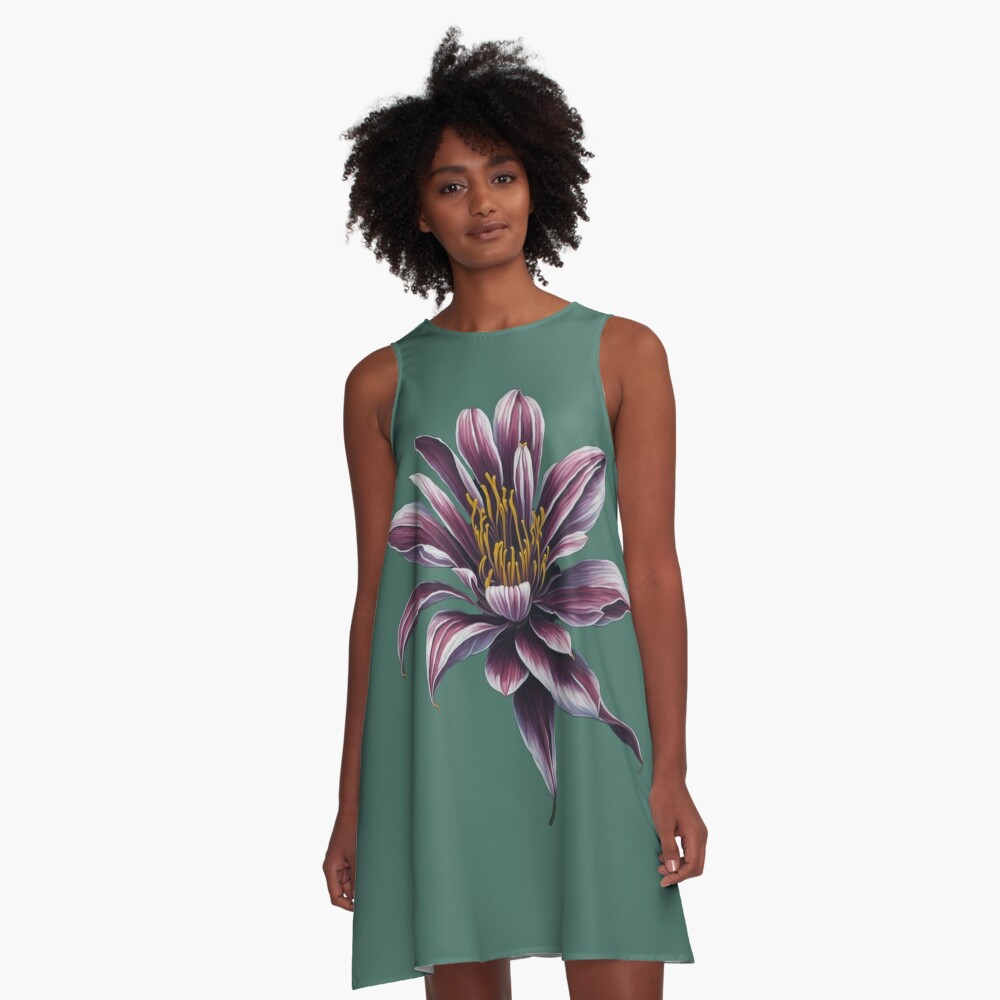
ERSHA DESIGN The beauty of the checkered lily flower A-Line Dress.
Sizes available XXS till 4XL
Loose swing shape for an easy, flowy fit.
Features
Sizes run large, so order a size down from your usual
Print covers entire front and back panel with your chosen design, by an independent artist
97% polyester, 3% elastane woven dress fabric with silky handfeel
Note that due to the production process, the placement of the print may vary slightly from the preview
A-Line dresses are made in the USA
The checkered lily, scientifically known as Fritillaria meleagris, is a charming and distinctive flowering plant belonging to the family Liliaceae. It is native to various parts of Europe, including the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and the Netherlands. The flower is also commonly referred to as the snake’s head fritillary or chess flower due to its unique checkered or chessboard-like pattern on the petals. Here are some key features and facts about the checkered lily: Appearance: The checkered lily is a perennial herbaceous plant that typically grows up to 30-40 centimeters (12-16 inches) in height. It has slender, graceful stems topped with a solitary, bell-shaped flower. The flower’s six petals are distinctively patterned with a checkered or mottled pattern of purplish-brown or maroon on a pale pink, white, or purplish base color. Habitat and Growing Conditions: Checkered lilies are often found in wet meadows, grasslands, and damp woodlands. They prefer slightly acidic to neutral soils and thrive in areas with moderate moisture levels. The plant’s natural habitat includes regions with cool climates and mild winters. Symbolism and Cultural Significance: The checkered lily holds cultural significance in various European countries. In the United Kingdom, it is associated with the county of Oxfordshire and is the county flower. It has also been used as a symbol of conservation efforts, as it is a protected species in some regions due to declining populations. Life Cycle: Checkered lilies are perennial plants, meaning they live for multiple years. They grow from bulbs, which are underground storage organs. The plants emerge in early spring, and the flowers bloom from April to May, depending on the specific region and climate. After flowering, the plant’s foliage dies back, and the energy is stored in the bulbs for the following year’s growth. Pollination: The checkered lily is pollinated by bees, particularly bumblebees. The bell-shaped flowers produce nectar as a reward for pollinators. The distinctive pattern on the petals may act as a visual guide, attracting bees and helping them locate the nectar-rich flowers. Conservation Status: Due to habitat loss and changes in land use, checkered lilies have experienced population declines in many areas. In response to this, conservation efforts have been implemented in certain regions to protect and preserve these beautiful flowers. It is important to respect their natural habitat and avoid picking or disturbing them in the wild. The checkered lily’s unique appearance and cultural significance make it a beloved and sought-after flower for gardeners and nature enthusiasts. Its distinctive pattern and early spring blooms add a touch of elegance to gardens and meadows, making it a delightful addition to any landscape.