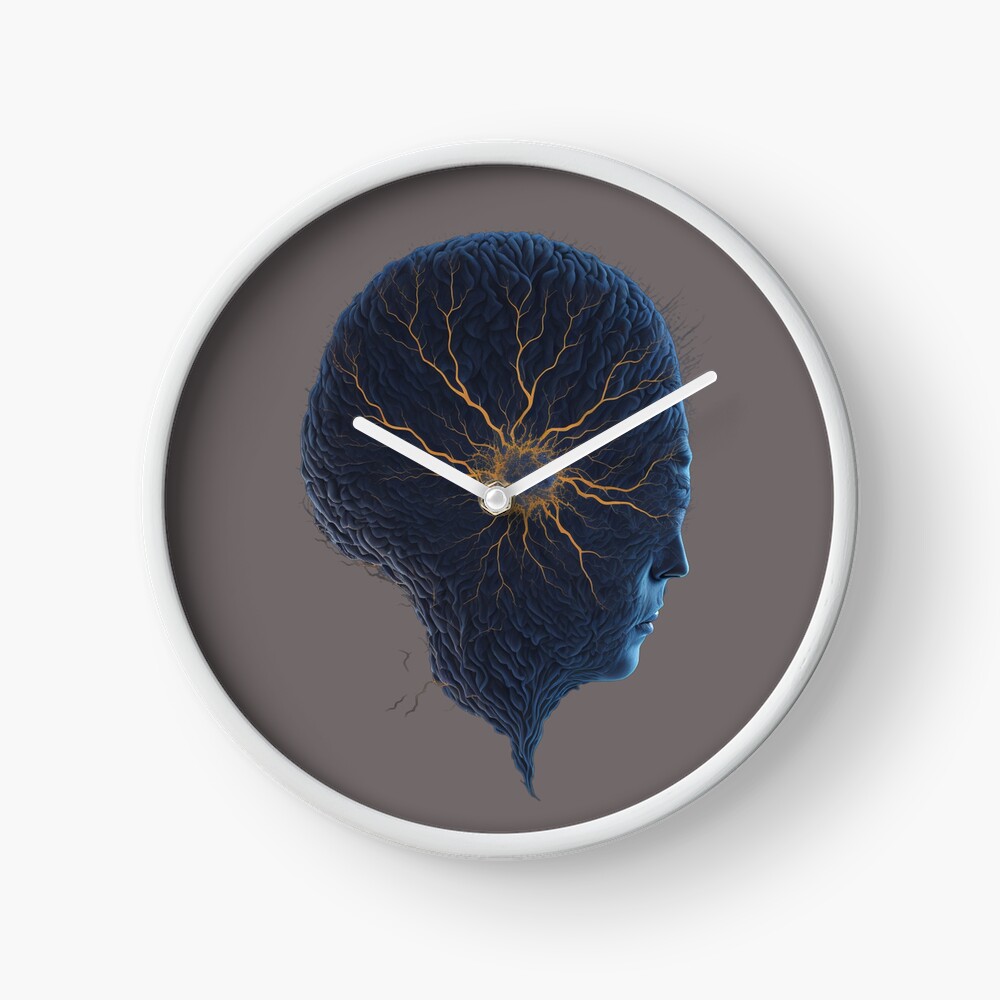
Description
ERSHA DESIGN It all comes together, clock.
Metal hands in black, white, red or blue.
Bamboo wood frame in black, white, or natural finish.
More Features
It’s always art o’clock when your clock is a work of art
Printed polypropylene face made for you when you order
Quartz clock mechanism for accurate timekeeping
Clear plexiglass lens
Built-in rear hook, ready to hang
AA battery not included
The brain is a remarkable organ that plays a central role in our body’s functioning and our experience of the world. It serves as the control center for all of our thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and bodily functions. While our understanding of the brain is still evolving, here are some key aspects that contribute to how it all comes together: 1. Neurons: The brain is composed of billions of specialized cells called neurons. These neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals, forming intricate networks. 2. Neurotransmitters: Neurons transmit signals across the tiny gaps called synapses using chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in various brain functions, including mood regulation, learning, and memory. 3. Brain regions: The brain is divided into different regions, each responsible for specific functions. For example, the frontal lobe is associated with decision-making and problem-solving, while the occipital lobe is involved in visual processing. 4. Neural circuits: Neurons form interconnected circuits within the brain, enabling the transmission of information between different regions. These circuits are responsible for complex processes such as perception, language, and motor control. 5. Plasticity: The brain exhibits a remarkable ability to adapt and change throughout life, known as neuroplasticity. It can reorganize its structure and function in response to experiences, learning, and environmental factors. 6. Integration of sensory information: The brain receives and integrates sensory information from various sources, including vision, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. It processes this information to create our perception of the world around us. 7. Higher cognitive functions: The brain is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as attention, reasoning, problem-solving, and memory. These functions involve the coordination of multiple brain regions and complex neural processes. 8. Emotions and social interactions: The brain also plays a crucial role in regulating emotions and processing social interactions. Areas like the amygdala and prefrontal cortex are involved in emotional responses and social behavior. 9. Homeostasis: The brain helps maintain the body’s internal balance through homeostatic mechanisms. It regulates functions like body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep to ensure optimal physiological conditions. 10. Consciousness: Although the nature of consciousness remains a subject of ongoing research and philosophical debate, the brain is believed to play a fundamental role in generating our subjective experience of consciousness. Understanding how all these aspects come together is a complex and ongoing scientific endeavor. Researchers from various fields, including neuroscience, psychology, and cognitive science, continue to explore the intricacies of the brain to unravel its mysteries.